Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or...
Read More- 5763 Stevenson Blvd, Newark, CA 94560
- +1 (510) 656-5700
Want to know about AED Urgent Care’s response to COVID-19? LEARN MORE
At AED urgent care clinic! We understand that urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be uncomfortable and disruptive to your daily life.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
A UTI is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. It occurs when bacteria, usually from the digestive tract, enter the urinary system and multiply, leading to inflammation and infection. UTIs are more common in women than men, but both can be affected.
Causes and Risk Factors:
UTIs most commonly result from the overgrowth of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), in the urinary tract. The following factors increase the risk of developing a UTI:
Gender: Women have a shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
Menopause: Reduced estrogen levels can lead to changes in the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection.
Urinary tract abnormalities: Structural issues in the urinary system can make UTIs more likely.
Catheter use: Inserting a urinary catheter raises the risk of infection.
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can contribute to UTI development.
Weakened immune system: Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or certain medications, increase susceptibility to infections.
Common Symptoms: The symptoms of a UTI can vary but often include:
Pain or a burning sensation during urination
Frequent urge to urinate
Passing small amounts of urine frequently
Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
Pelvic pain or discomfort
Fatigue or general malaise
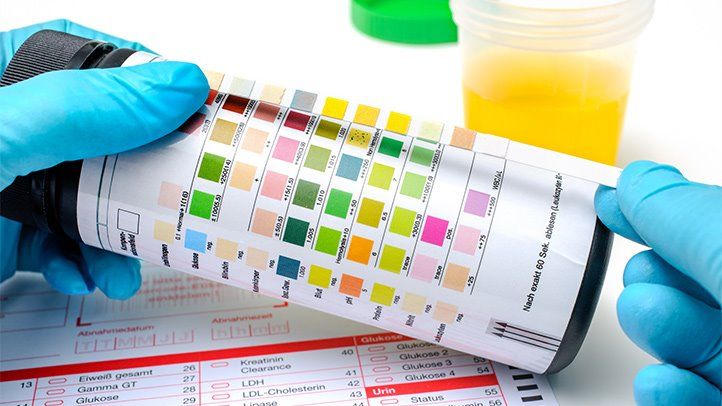
Diagnosis: If you suspect a UTI, it is essential to visit our urgent care clinic for a diagnosis. Our experienced healthcare professionals will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may involve:
Reviewing your medical history and symptoms
Performing a physical examination
Collecting a urine sample for analysis, including a urinalysis and urine culture, to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment: Once diagnosed with a UTI, appropriate treatment will be recommended based on the severity of your infection. Common treatment options include:
Antibiotics: Prescribed to kill the bacteria causing the infection. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed.
Pain relief: Medications to alleviate discomfort, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Increased fluid intake: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
Prevention strategies: Our healthcare professionals may provide guidance on lifestyle changes or preventive measures to reduce the risk of recurrent UTIs.
When to Seek Urgent Care:
While UTIs can often be managed with prompt treatment, there are instances when urgent care is necessary. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Severe pain or abdominal pain
High fever or chills
Vomiting or nausea
Signs of kidney infection, such as back pain or flank pain
Any worsening symptoms or concerns about your condition
Receiving a COVID-19 vaccine is the most effective and safest measure to prevent severe illness. Similar to other vaccines, the COVID-19 vaccine instructs your body on building its own defense against the virus responsible for this disease. Typically, the COVID-19 vaccine consists of two doses, with the second dose administered 14 to 28 days after the initial one. It takes approximately three weeks after the final dose to develop immunity. Access to COVID-19 vaccination is subject to availability and regulations set by your state. Please reach out to us for further information on obtaining a COVID-19 vaccine.